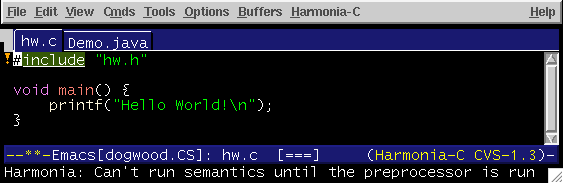
Harmonia-Mode User's Guide
Printer-Friendly Version | HTML Version |
Introduction
This is the first public software release for the Harmonia project. It consists of Harmonia-Mode, a demonstration application for the Harmonia Framework. Harmonia-Mode is an editing mode for XEmacs, like java-mode and c-mode. It demonstrates a set of enhanced editing features enabled by the Harmonia Framework.
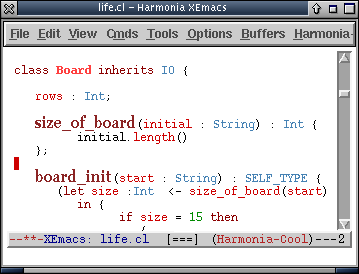
An example of Harmonia-Cool-Mode
Harmonia-Mode
Harmonia-mode provides editing features to your XEmacs document as you're editing. Some of these features include syntax highlighting, proper (Emacs-style) indentation, visual indications of compile errors, and pop-up menus that provide semantic information (such as the definition of a particular symbol). No doubt, you have have seen many of these features provided by higher-end commercial editors, such as Visual Studio, Eclipse or Metrowerks CodeWarrior. In the Harmonia-mode world, however, we don't stop there. Harmonia-mode also provides you with structural browsing, navigation and search capabilities, and structural elision (on a buffer-by-buffer basis for this first version). Best of all, Harmonia-mode is language-independent, meaning that support for a particular programming language is provided via plugin module, giving the programmer access to all of these features in any language in which he or she wishes to program.
Harmonia Language Support
Harmonia supports the following languages in this second release.
| Language |
Versions Supported |
| C |
C99, GNU C |
| Java |
Java 2 v1.4.2 |
| Scheme |
R5RS |
| Cool |
2002 (used in CS164 compiler course at UC Berkeley) |
| Titanium |
2.630 (September 2004) |
We are planning to support many more languages in the future. Not yet released, but in various stages of development are language plug-ins for Cobol, Common Lisp, C++, JavaScript, Regular expressions, SRCL (used in IBM ViaVoice), Tcl, and XML.
How Harmonia Works
Harmonia runs three compiler analyses on your XEmacs buffer: lexing, parsing (syntax) and semantic analysis. Conceptually, all of these analyses happen on every keystroke (actually, they occur at varying times between keystrokes). Thus, it is important to make the analyses fast, so they don't get in the way. Both lexing and parsing are incremental, meaning they take time proportional to the size of the change you make. Semantics is non-incremental (currently), but in the languages supported does not take any perceptible amount of time (less than 20-30 ms on average).
Using the results of these analyses, Harmonia-mode
will supply you with syntax highlighting, indentation,
error-detection, and a few other features. Note that
you won't gain the benefit of some of these features
in sections of your program that are not syntactically correct. Syntax highlighting uses lexical (non-structural) information, and will most often exist and appear to be correct. Indentation has been engineered to use lexical information when the syntax tree is not available. Error detection and other services are usually based on Harmonia's access to the parse tree of your program, thus they will only work in areas of your program that are (or were) syntactically correct. Harmonia-mode remembers the structure of your program as you edit it, but if you type a new method declaration from scratch, it won't know what type signature it has until you type the last semicolon.
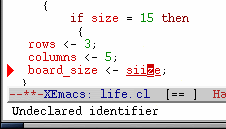
siize is a misspelled identifer in Harmonia-Cool-Mode
Just like a C, Java, Titanium or Cool compiler (or Scheme interpreter/compiler), Harmonia-mode will not be able to run its semantic analyses unless the syntax analysis ran without finding errors.
Note: Harmonia-Mode is not a replacement for a compiler. Harmonia-Mode will not generate code, nor will it plug into the backend of your compiler to do so. All analyses performed in Harmonia-Mode are used only within the editor.
The Future
In the future, we will be releasing the full source code for Harmonia, including the tools we use to build language modules. This will enable you to write language modules for your own languages, as well as see how we designed and implemented our analysis technology.
Installation and Setup
Download
Please download Harmonia from our download page. These instructions are for the binary release of Harmonia.
Running Harmonia-Mode
- To run Harmonia-mode, just run xemacs from your shell.
- Note that
xemacs is not the same as emacs! Harmonia-mode doesn't work with regular emacs, so make sure that you run xemacs.
- You will be able to tell that you ran the right program if you see Loading Harmonia...done in the bottom line of your XEmacs window. If you do not see this message, it may have been overwritten by a later one. Look for it in the Message Log (Choose the Show Message Log menu item from the View menu).
- To run Harmonia-mode, just double-click on Harmonia-XEmacs in your /Applications folder.
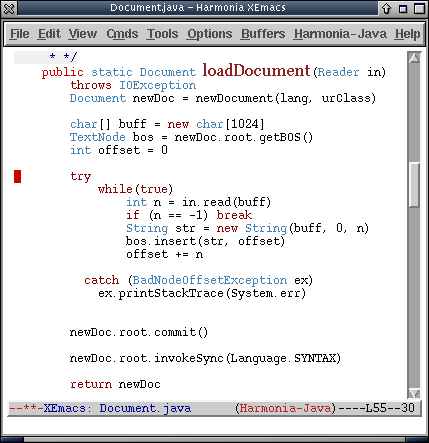
Harmonia-Mode comes with a demo directory in /usr/harmonia/demo (on MacOS X it is /Library/Application Support/Harmonia/demo), inside of which are example programs in each language that this release supports. Load a C file (ending in ".h" or ".c"), a Java file (ending in ".java"), a Scheme file (ending in ".scm"), a Titanium file (ending in ".ti"), or a Cool file (ending in ".cl") and start editing! You should see Harmonia-C, Harmonia-Java, Harmonia-Scheme, Harmonia-Titanium or Harmonia-Cool at the bottom of your window in the modeline. Try them out!
To see what you can do with Harmonia-Mode, read the Features section of this manual (Language Analyses, Indentation and Highlighting, Structural Movement, Structural Search, and Elision).
If you decide to stop using Harmonia-mode, you can switch to the fundamental XEmacs editing mode by typing M-x fundamental-mode. For a more permanent solution, see the next page: Turning it On.
Additional Setup for Harmonia-mode for C
Harmonia-C-Mode uses the C preprocessor. If your preprocessor is not installed in its standard location for your platform, you will need to configure Harmonia to know where it is.
Additional Setup for Harmonia-mode for Java
On Linux and Solaris, Harmonia-Java-Mode needs access to the Java runtime source code in order to properly analyze your Java files. You will need to configure Harmonia to know where to find it.
Troubleshooting
- XEmacs starts but I don't see the message that Harmonia has loaded.
- There may be something in your ~/.xemacs/init.el (or ~/.emacs) file that has an error with XEmacs. This may prevent Harmonia-Mode from loading. Check out your XEmacs startup files and try to fix the problem.
- I loaded a Java file, but Harmonia-Mode does not start.
- Harmonia-Mode is too slow to use on really large files. We disable it on files larger than 200K. You can change this value by configuring Harmonia.
- I loaded a Titanium file that ends in .java, but it starts in Harmonia-Java-Mode, not Harmonia-Titanium-Mode.
- Titanium files must end in .ti to be autodetected by Harmonia-Mode. To switch modes manually, type
M-x harmonia-titanium-mode.
Crash Recovery and Bug Reporting
Harmonia-mode has been engineered to recover from crashes in order to preserve your work, and to help us with debugging. If it crashes, it will ask for permission to file a bug report (via email to harmonia-bugs@sequoia.cs.berkeley.edu). (Note: sending email will not work on MacOS X).
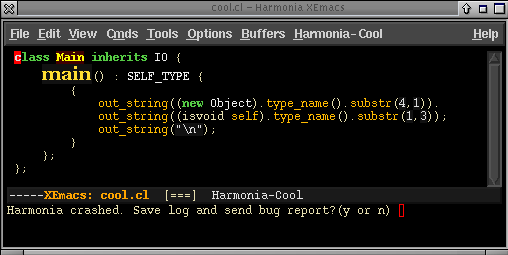
Harmonia-mode will then restart itself on your buffer, and allow you to edit your program again.
If you have any other problems with Harmonia-Mode, please report them using M-x harmonia-report-bug, or send us email at harmonia-bugs@sequoia.cs.berkeley.edu. Harmonia-mode is currently in active development, and we will be updating these web pages to notify you as we fix bugs and add features.
Turning on Harmonia-Mode
In order to use Harmonia-Mode, it must be enabled for each file you edit. By default, Harmonia-Mode is enabled for all files it supports:
| Extension |
Harmonia Language |
.java |
Harmonia-Java-Mode |
.c |
Harmonia-C-Mode |
| .h |
Harmonia-C-Mode |
| .scm |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode |
.cl |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode |
.ti |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode |
You can tell whether or not Harmonia-Mode is enabled for a file you are editing in XEmacs by looking for the word "Harmonia-language" on the modeline (the bar at the bottom of the XEmacs window):
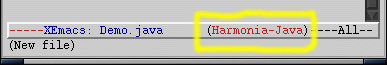
Harmonia-Mode can be enabled either automatically (based upon the file's extension), or on a manual, per-file basis.
Automatically Enabling Harmonia-Mode
Harmonia-Mode's customization system includes an option to automatically enable or disable Harmonia-Mode for files of specified extensions. For more information, see the customization documentation.
Manually Enabling Harmonia-Mode
To manually enable Harmonia in a file being edited, switch to the buffer containing the file and type M-x harmonia-language-mode.
Examples:
| Command |
Enables Mode |
M-x harmonia-java-mode |
Harmonia-Java-Mode |
M-x harmonia-c-mode |
Harmonia-C-Mode |
M-x harmonia-scheme-mode |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode |
M-x harmonia-cool-mode |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode |
M-x harmonia-titanium-mode |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode |
Automatically Disabling Harmonia-Mode
The current version of Harmonia-Mode runs (really) slowly on large files. We respect a user-defined file size limit when deciding whether to enable Harmonia-Mode on a particular file. By default, the limit is 200,000 bytes. If Harmonia-Mode does not start up automatically, please check that your file is smaller than this limit. Otherwise, you can extend the limit by using Harmonia's customization feature.
Manually Disabling Harmonia-Mode
You can always change back to a standard XEmacs mode by typing M-x java-mode, M-x c-mode, M-x scheme-mode, etc. appropriately (there is no regular XEmacs Cool or XEmacs Titanium mode, but for these you can use M-x fundamental-mode).
Analyses
Harmonia-Mode utilizes source code analyses to provide many of its services. This section describes these analyses and how they affect the user.
The Three Phases of Analysis
Harmonia has three phases of analysis: Lexical, Syntax, and Semantic. After every user-edit, Harmonia-Mode initializes three "idle timers" (described below) that wait for specified amounts of idle time to pass before executing each of the three analyses.
Lexical Analysis: The Lexer
Lexical analysis is the most lightweight of the three analyses. It organizes character-sequences into separate words, and uncovers most of the information used for syntax-highlighting.
For instance, if a user were to type "private int x;" then the lexer would break it up into the words "private" "space" "int" "space" "x" ";" and would determine that "private" is a keyword to be bold-blue, that "int" is a type to be italicized-grey, and that "x" is an object identifier.
Syntax Analysis: The Parser
The job of the parser is to uncover the structure of programs. For example, it determines, in Java, that the sequence of words "private" "space" "int" "space" "x" ";" is a variable declaration.
Syntax analysis is needed for most Harmonia-Mode features (those that contain "structure" in their names). It also is needed for the syntax-highlighting of a few constructs, like function names.
Semantic Analysis
The main job of semantic analysis is to determine the names and types of program structures, and to verify their correctness. Consequently, this is the phase of analysis which will uncover type and name errors.
The implementation of semantic analysis varies
considerably among the supported languages (since every programming language has a unique definition), so it is important to understand its features and limitations for the language in which you are working. See the Languages section for more information.
Analysis Indicator
The current state of the analyses is visible on the XEmacs mode-line. A program can be in any one of four analyzed states:
| Modeline Visual |
Completed Analyses |
 |
None |
 |
Lexical |
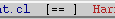 |
Lexical, Syntactic |
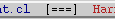 |
Lexical, Syntactic, Semantic |
Some languages in Harmonia do not currently support semantic analysis. Files in these languages have shorter analysis indicators, like this: 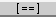 .
.
Semantic Context Menus
You can browse Harmonia-Mode's semantic information by right-clicking on function names, class names, variables and constants that you're interested in. Doing so invokes a contextual menu that displays information about the code you clicked on and gives you links to semantically related sections of the program.
For instance, in a Java program containing the statement return x + 3;, you could right-click on x to invoke the following menu:
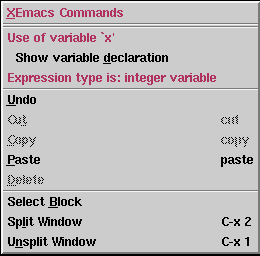
In this case, clicking on "Show variable declaration" would open the file containing the definition of the variable x and put the cursor on it.
Incrementality
Harmonia-Mode re-analyzes after each keystroke, once a specified amount of time has passed (usually less than a second). This per-keystroke analysis would be too slow on large files if Harmonia-Mode's analyses were not incremental. To retain snappy response times, Harmonia-Mode only re-analyzes the portions of the program which have changed.
The most fundamental analyses, lexical analysis and syntax analysis (parsing), are both fully incremental. Semantic analysis, unfortunately, is usually not incremental, since a change in one region of a file might potentially impact the analysis of code in any other region. For example, renaming a variable declaration can cause errors in any region of code that references the changed variable. Therefore, semantic analysis may be somewhat slow on larger files.
Scheduling the Analyses during Interactive Use
Analysis results beyong lexing are not very useful to display while the user is actively typing, so we delay running the analysis on the assumption that a pause in typing indicates a logical time to run the analysis.Each of the three analyses each have customizable idle times that delay their execution. The analyses run in sequence after every user-edit, pausing between each analysis until the user has been idle for a the specified amount of time.
Here are the default idle times for each analysis:
| Analysis |
Time |
| Lexical |
0.001 seconds |
| Syntax |
0.5 seconds
|
| Semantics |
0.4 seconds
|
If the execution of Harmonia-Mode analyses are causing unwanted pauses, increasing the values of these idle times will probably improve things. For more information on how to do so, see the settings section.
Indentation and Highlighting
This section describes Harmonia-Mode's automatic indentation and highlighting systems.
Indentation
Harmonia-Mode can automatically indent the lines of your source code. Harmonia-Mode supports proper (Emacs-style) indentation. If you press tab on a particular line, no matter where on that line, it will indent the line to its proper location, given its context. (By constrast, improper indentation is what you get from a word processor. When you press tab, it inserts a tab at your cursor location no matter what context you are in. While fine for writing poetry, this is not so useful for writing programs.)
Harmonia-Mode's indentation system behaves similarly to XEmacs' system (or at least, we tried to make it behave that way), but is implemented completely differently. Instead of XEmacs' reliance on inexact textual heuristics, we use the tokenization and syntactic structure that Harmonia maintains for each document to provide precise, correct, information to the incremental indentation engine. This engine is programming language-independent; for each programming language that Harmonia-Mode supports, there is a corresponding XML-based indentation specification file (installed in /usr/harmonia/etc) that describes how to indent a particular line in a variety of contexts.
All of XEmacs' indentation commands, such as indent-region, are overridden with Harmonia-Mode's indentation algorithm as well. In this first release of Harmonia-Mode, we have not given you enough documentation to write your own indentation specifications, but feel free to take a look and tinker with it.
Syntax Highlighting
Harmonia-Mode supports syntax highlighting. The decision of what to highlight is undertaken by our own language-specific highlighting specification. Again, instead of relying on XEmacs' reliance on on inexact textual heuristics (regular expressions), Harmonia-Mode uses our precise tokenization and syntactic (where appropriate) information to color tokens. Each programming language's specification is written in a Lisp-like notation (though for this release, is uncustomizable by the user.)
Harmonia-mode uses more faces than font-lock does, each of which may be customized to your liking.
Error and Warning Display
When one of Harmonia-Mode's analyses discover an error in the program (something that a compiler would catch), it informs the programmer by underlining the invalid region and pointing at it with a triangle in the left margin. Compiler warnings are indicated in a different color and marked by an exclamation mark icon.
Moving the mouse cursor or text cursor over the error region causes an explanation of the error to appear at the bottom of the XEmacs window.
As soon as the programmer fixes the error or warning, the underline will disappear from view.
See the customization section for information on changing the way errors and warnings are displayed.
Structural Movement
Structural movement is the ability to move the cursor in terms of program structures instead of characters. For example, instead of moving the cursor to the next character in a file, one might move to the next function definition.
Harmonia-Mode has two different forms of structural movement: structure browsing, and structure jumping.
Structure Browsing:
Harmonia-Mode implements a novel structure-aware cursor, similar to the one used in the Pan research project. This feature allows a programmer to navigate hierarchically throughout a program's source code.
When using this type structural movement, a highlighted region appears with the cursor, indicating the programming structure being browsed. The user can move this structure forward, backward, or make it bigger or smaller.
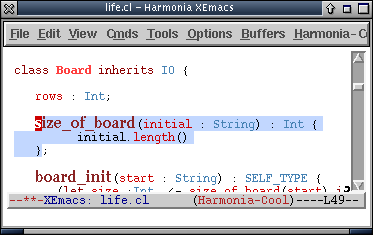
In this example Cool file, the cursor is the dark red rectangle, and the light-blue region around the "size_of_board" method indicates that it is the current structure being browsed.
Using the Structure Browser:
When structure-browsing, the programmer can navigate:
- larger in the hierarchy, selecting a larger enclosing structure
- smaller, selecting the first sub-structure of the current structure
- forward, selecting the next structure at the same level as the current structure
- or backward, selecting the previous structure at the same level.
The four commands just described are available in the "Structure Browse" sub-menu:
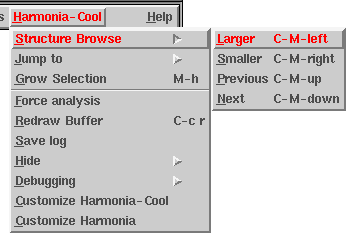
Using the menu is inconvenient, however, for any intensive structural navigation. It is recommended that you use it only as a reference to remember the structure browsing keyboard bindings: C-M-left, C-M-right, C-M-up, and C-M-down.
Structure Browsing sessions involve three steps:
- Enable: Executing any of the four structure browsing commands will automatically enable structure browsing and highlight the current structure.
- Browse: When structure browsing, the user can continue to use the structure browsing commands to navigate their program's hierarchy.
- Disable: Once done, pressing any other key will disable structure browsing and remove the highlight.
Structure Browsing Examples:
- Structure-browsing is a quick way to move amongst method definitions in a file. For example, pressing C-M-up will take a programmer from this place in the file...

...directly to the method definition above it:
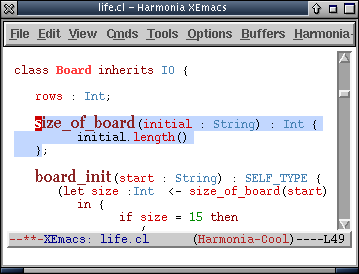
The programmer can then start editing that method, and the highlight will be disabled.
- It's easy to move among larger structures as well, as we see in this Java file:
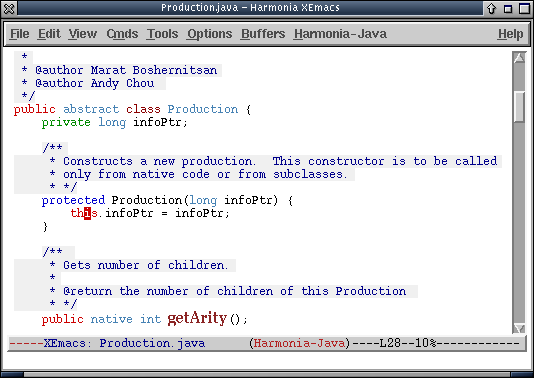
Pressing C-M-left C-M-left selects first the method definition encompassing the cursor, and then the class:
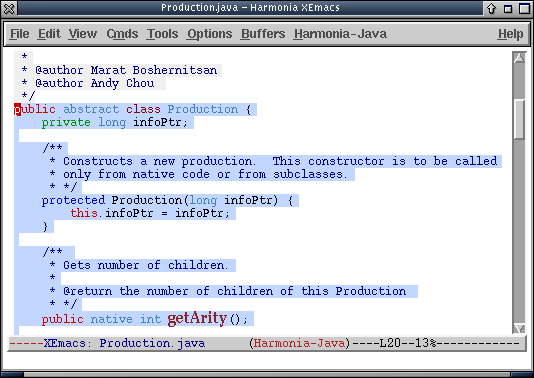
Now, pressing C-M-down C-M-down moves the programmer to the second class following the current one, leaving the programmer here:
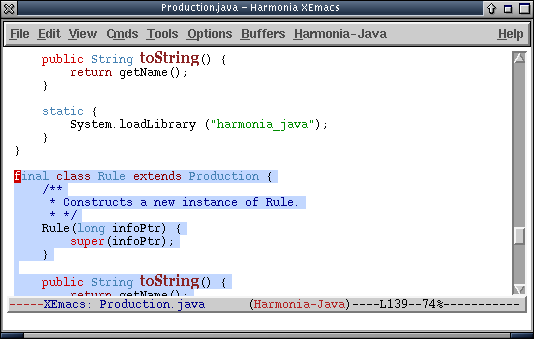
As always, the programmer can now immediately continue normal editing. As soon as he or she moves the cursor or types a keystroke, the highlight will be disabled.
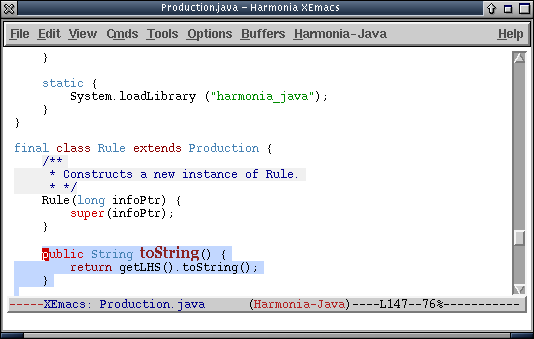
- Perhaps, though, the programmer now wants to edit the method "toString()" in this class.
Pressing C-M-right selects the first method in the class (the constructor "Rule()"), and then pressing C-M-down once brings the programmer directly to the desired method:
- Although we haven't shown any examples of it here, one can also browse the lower-level structures of their programs, such as method arguments, variable declarations, and the branches of "if" statements.
The "Jump to" Feature:
The "jump to" feature is a simpler alternative to the structure browser. With it, you can "jump" the cursor to the next or previous structure of certain types. Each language has a particular set of structure-types to which one can jump.
Using "jump to"
In the Harmonia menu, select "Jump to".
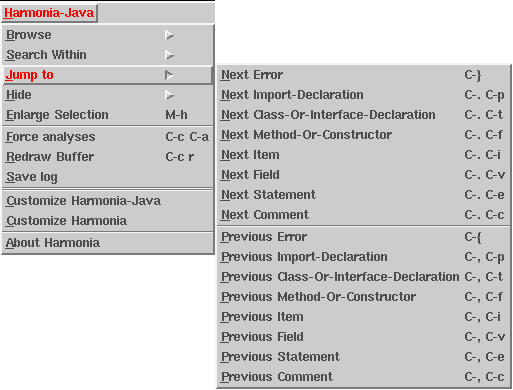
You will now see a list of program structures to which Harmonia knows how to jump. Selecting one of these items will move the cursor appropriately.
Note: Each item in the menu is listed with its corresponding keyboard shortcut, if available. Browsing these menus is a great way to learn Harmonia-Mode's key-bindings.
Structural Search
The XEmacs incremental search (I-search) feature has been extended in Harmonia-Mode by allowing you search for specific program features.
Using Harmonia's I-search
Original I-search
Just like with the XEmacs I-search, you can enter Harmonia's I-search mode by typing C-s (or C-r). The minibuffer will then display "I-search:". At this point, you can type any sequence of characters, and XEmacs will show you all strings in the current buffer that match the sequence you typed.
Harmonia-mode's I-search supports all the features of XEmacs' built-in I-search. For more information the built-in I-search, see the XEmacs User's Manual.
Harmonia's Filtered Searches
Harmonia-mode adds value to the regular I-search by allowing you to filter searches to return specific types of structures.
Each language has a variety of structure-types to which you can filter a search. There is a keybinding for each type, that you can use to toggle each type's filter.
- To filter the current search to a type of structure, enter the structure's filter command after entering I-search mode.
- Entering the command again will remove the filter.
- Entering the command for a different filter will remove the old filter before adding the new one.
(Note: This behavior is configurable. For more information, see "Persistent I-search Structure Filters" in the Customization Reference section.)
Example: Cool
Cool supports the following filter commands:
| Command |
Filters To |
M-t |
Class names |
M-m |
Method names |
M-v |
Variable names |
M-i |
Identifiers |
M-w |
Words |
M-c |
Comments |
| M-s |
Strings |
To search for the next occurrence of a method with a name containing foo, type C-s M-m foo.
To search for the previous occurrence of the word bar in a comment, type C-r M-c bar.
Example: Java
Java supports the following filter commands:
| Command |
Filters To |
M-t |
Class or Interface names |
M-m |
Method and Constructor names |
M-v |
Variable and Field Names |
M-i |
Identifier names |
M-w |
Words |
M-c |
Comments |
| M-s |
Strings |
To search for the next occurrence of a method with a name containing foo, type C-s M-m foo.
To search for the previous occurrence of the word bar in a comment, type C-r M-c bar.
Additional Languages
To see the Harmonia I-search commands for additional languages, see the Key Bindings Reference.
Elision
Harmonia-Mode has a feature that hides from view all structures of specified types. Each language has a list of structure-types that may be hidden when viewing files in the language. The list for each language is always available in the Harmonia-Mode menu under the "Hide" section:
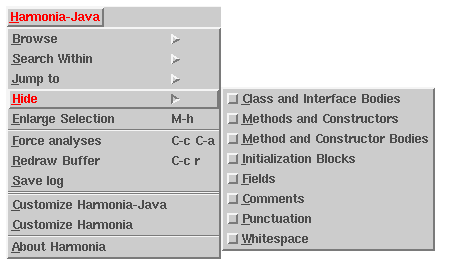
In this example, one can filter all comments from view by selecting "comments" from the menu.
Original Program:
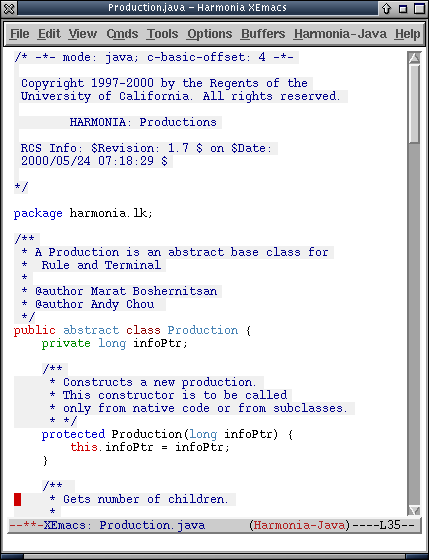
With Comments Hidden:
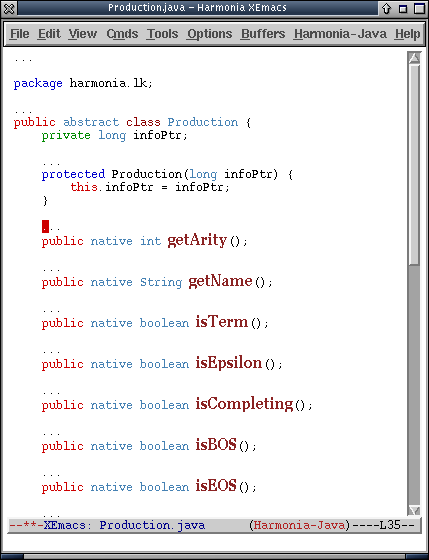
Notice that the comments are replaced with ellipses ("..."). Some filterable structures have other replacements. The next screenshot shows how punctuation is replaced with a space when hidden.
With Punctuation Hidden:
Future versions of Harmonia-Mode will improve upon this feature. For example, our structural pattern-matcher will enable a powerful user-specified view-filter (that a user could use to hide all debugging code, for instance), and a code-folding feature will allow users to elide specific, individual structures on-demand, rather than hiding all structures of a certain type at once.
Supported Languages
Harmonia-Mode's supported languages currently have varying features, analyses, and caveats. This page describes each language in detail.
Cool
Language version
Harmonia-mode supports Cool as used in the UC Berkeley CS164 course offering of Spring 2003.
What it will do
Harmonia will correctly detect all lexical, syntactic, and semantic errors. Syntax highlighting, structural selection, movement, elision and search, are all complete. Semantic context menus are complete, and supports use-def navigation, type introspection, display of class inheritance, and method name resolution.
Java
Language version
Harmonia-mode supports Java 2 v1.4.2 (as shown in The Java Language Specification Second Edition, (James Gosling, Bill Joy, Guy Steele and Gilad Bracha)). Harmonia-mode supports all current versions of the Java class library as of Java 2 v1.4.2.
What it will do
Harmonia will correctly detect all lexical, syntactic and almost all semantic errors. Syntax highlighting, structural selection, movement, elision and search, are all complete. Semantic context menus are complete, and supports use-def navigation (for types, constructors, methods, fields, local variables) and type introspection,
How it works
Harmonia assumes the standard directory layout defined in Section 7.2.1 of the Java Language Specification.
While Harmonia opens a file, it also loads (in the background) all the other files upon which it depends. The first time ever that it does so, it caches the semantic data. Therefore, you should expect a much longer delay the first time Harmonia consults a particular library file. Harmonia provides a read-only semantic data cache for the JDK version 1.4.2. If Harmonia-Java looks for a file and does not find it, but it is present in the read-only cache, the cache file is used.
The directory "." (i.e. the current directory), does not make much sense when you are in an editor. Therefore, the directory "." is
interpreted as the directory containing the particular file
being examined if it is not in a named package; otherwise it is
the directory up the hierachy as many levels as there are
package levels for named packages.
For example, suppose you have
a file ~/mycode/Foo.java with the code:
- public class Foo {
- void m() { new Bar(); }
- }
The directory "." will be interpreted as
~/mycode/. Semantics will search this directory for the file Bar.java.
Now suppose you have
a file ~/mycode2/myPackage/Foo.java with the code:
- package myPackage;
-
- public class Foo {
- void m() { new myPackage.Baz(); }
- }
The directory "." will be interpreted as
~/mycode2/. Semantics will search this directory for the file myPackage/Baz.java.
This interpretation attempts to approximate the behavior of javac.
At this time, there is no provision for "projects". Thus, all open files are considered for semantic information for all other open files. This can lead to strange results at times, with things being defined when one would not think they ought to be. If something does not seem to be behaving properly, check all other open buffers. Another consequence is that you must manually change classpaths if you have two sets of files with the same classes defined.
Bugs
Harmonia does not check definite assignment and some dataflow information. If you discover any other bugs, please report them with M-x harmonia-report-bug.
Titanium
Language version
Harmonia-mode supports a superset of Titanium, as described in the Titanium Reference Manual 1.11.
What it will do
Harmonia will correctly detect all lexical, syntactic and almost all semantic errors. Syntax highlighting, structural selection, movement, elision and search, are all complete. Semantic context menus are complete, and supports use-def navigation (for types, constructors, methods, fields, local variables) and type introspection.
How it works
Harmonia for Titanium functions similarly to Harmonia for Java, with a few differences.
Harmonia provides a read-only semantic data cache for the TDK version corresponding to version 1.16 of the language reference.
Titanium projects often have files ending in .java. If these files are not in Titanium mode, Harmonia for Titanium will not notice them. To use Java files for Titanium, type M-x harmonia-titanium-mode.
Templates are not type checked beyond information necessary for instantiations, because it is not clear how semantic errors are to be checked and then reported to the user.
The Titanium Reference describes Titanium without nested classes. Harmonia for Titanium is based on Harmonia for Java, and so is a superset of the union of Titanium (based on Java 1.1) and Java 1.4. The Titanium compiler also allows nested classes. Unfortunately, these two versions of nested classes are incompatable in some ways. Please report any incompatability as a bug, as it is unknown all the ways that they differ.
The variables that hold the classpaths for Java and Titanium are different.
Bugs
Harmonia will not cache files containing templates. This is due to compile time constant information from template formals, which is not readily cacheable. Harmonia does not check definite assignment and some dataflow information, nor is single implemented. If you discover any other bugs, please report them with M-x harmonia-report-bug.
C
Language version
Harmonia-mode supports C99 with most GNU extensions.
What it will do
Harmonia will correctly detect all lexical, syntactic and semantic errors. Syntax highlighting, structural selection, movement, elision and search are all complete. Semantic context menus are complete, and support use-def navigation (for types, enums, structs, unions, variables), type introspection, and navigation from 'goto' statements to their targets. In addition, when you move the mouse over an entity in your program, the type of the entity will appear in the modeline.
Preprocessor
Harmonia supports a subset of the C preprocessor through a menu item in the Harmonia-C menu. Before using this for the first time, make sure you have set up the customize variables for the running the C preprocessor on your local computer. To run the preprocessor, pick the menu item Run Preprocessor. Harmonia will execute the preprocessor and insert the contents of #include statements into the buffer (marked invisible and read-only), and will then reanalyze the buffer. Since the #includes are usually very big, Harmonia-Mode will take some time to run its analyses (for the first time).
To see the preprocessed include text in your buffer, pick the menu item, Show Preprocessed Includes. To hide them again, choose the same menu item again. To delete the preprocessed part of the file, pick the menu item, Delete Preprocessed Includes.
If you edit your #include line, for example, by changing <>'s to quotes, or by changing the file that you're loading, the preprocessor information will be out of date. A compiler warning will appear saying that since you changed a #include, semantics is now turned off. You should pick the menu item Rerun Preprocessed Includes to get rid of the preprocessor information and rerun the preprocessor for the up-to-date information.
Scheme
Language version
Harmonia-mode supports R5RS Scheme with MIT Scheme extensions for escape characters within strings. Harmonia-mode does not support keywords (special forms) to be used as identifiers. R5RS discourages this practice, but does not outright forbid it. In addition, Harmonia-mode does not parse/evaluate Scheme define-syntax macros. Lisp-style macros (quasiquote, comma and comma-at) are supported.
What it will do
Harmonia will correctly detect all lexical and most syntactic errors in Scheme. Harmonia does not analyze Scheme semantics.
Bugs
Harmonia-mode allows Scheme definitions (in 'let', 'let*', 'letrec', 'define' and 'lambda') to have a blank body, but does not tell the user that this is illegal Scheme. Future versions of Harmonia-mode will detect this error and issue a warning to the user. Harmonia-mode does not properly count the number of nestings of quasiquote and commas to verify that they match up.
XEmacs Keybindings
This page lists all user-level commands provided by Harmonia-Mode. It is divided into the following subsections:
Except for the I-Search filters, any of the commands listed below can be invoked with their keybinding or with M-x [command]. For example, typing M-x harmonia-mode will invoke the harmonia-mode command.
The I-Search filters are applied by first entering I-Search mode (with C-s or C-r), and then by entering the particular filter's I-Search command, specified below.
All Languages
| Command |
Keybinding |
Description |
| harmonia-mode |
|
Switches to harmonia-<language>-mode on the current buffer, auto-detecting the language |
| harmonia-structure-browse-larger |
C-M-left
C-M-u |
Structure-browses to the structure enclosing the current structure, or initiates structure-browsing at an enclosing structure |
| harmonia-structure-browse-smaller |
C-M-right
C-M-d |
Structure-browses to the current structure's first sub-structure, or initiates structure-browsing at an enclosing structure |
| harmonia-structure-browse-next |
C-M-down
C-M-n |
Structure-browses to the next structure of the same size as the current structure, or initiates structure-browsing at a following structure |
| harmonia-structure-browse-previous |
C-M-up
C-M-p |
Structure-browses to the preceding structure of the same size as the current structure, or initiates structure-browsing at a preceding structure |
| harmonia-refresh |
C-c C-r |
Redraws the text of the XEmacs buffer from Harmonia's internal data structures |
| harmonia-force-analyses |
C-c C-a |
Forces all analyses to be run immediately |
| harmonia-grow-region-to-branch |
M-h |
Enlarges the current XEmacs region (selection) to select the smallest structure enclosing the region, or the current cursor location if the region is inactive. |
| harmonia-undo |
C-x u
C-_
C-/
<undo> |
Reverts the buffer to a previous version in the same way as XEmacs' undo, but uses Harmonia's history mechanism rather than XEmacs' (Note: also bound to C-_, C-/, and <undo>) |
| harmonia-goto-next-error |
C-} |
Moves the cursor to the first syntactic or semantic error following its current location |
| harmonia-goto-previous-error |
C-{ |
Moves the cursor to the first syntactic or semantic error preceding its current location |
| harmonia-save-log |
|
Saves a log of all edits into the file <filename>.hlog |
| harmonia-report-bug |
|
Enables user to send a bug report to harmonia-bugs@sequoia.cs.berkeley.edu |
Java
| Command |
Keybinding |
Description |
| harmonia-java-mode |
|
Switches to harmonia-java-mode in the current buffer |
Harmonia-Java-Mode I-Search
| Command |
Filters To |
Description |
C-s M-t |
Class and Interface names |
Filter the current interactive search to class or interface names |
C-s M-m |
Method and Constructor names |
Filter the current interactive search to method or constructor names |
C-s M-v |
Variable and Field names |
Filter the current interactive search to variables and field names |
C-s M-i |
Identifier names |
Filter the current interactive search to identifiers |
C-s M-w |
Words |
Filter the current interactive search to tokens |
C-s M-c |
Comments |
Filter the current interactive search to comments |
| C-s M-s |
Strings |
Filter the current interactive search to strings |
Titanium
| Command |
Keybinding |
Description |
| harmonia-titanium-mode |
|
Switches to harmonia-titanium-mode in the current buffer |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode I-Search
| Command |
Filters To |
Description |
C-s M-t |
Class, Interface and Immutable names |
Filter the current interactive search to class, interface or immutable names |
C-s M-m |
Method and Constructor names |
Filter the current interactive search to method or constructor names |
C-s M-v |
Variable and Field names |
Filter the current interactive search to variables and field names |
C-s M-i |
Identifier names |
Filter the current interactive search to identifiers |
C-s M-w |
Words |
Filter the current interactive search to tokens |
C-s M-c |
Comments |
Filter the current interactive search to comments |
| C-s M-s |
Strings |
Filter the current interactive search to strings |
C
| Command |
Keybinding |
Description |
| harmonia-c-mode |
|
Switches to harmonia-c-mode in the current buffer |
Harmonia-C-Mode I-Search
| Command |
Filters To |
Description |
C-s M-m |
Function names |
Filter the current interactive search to function names |
C-s M-n |
Symbol definition names |
Filter the current interactive search to symbol definitions |
C-s M-t |
Struct, Union, and Enum names |
Filter the current interactive search to structure, union, and enumeration names |
C-s M-w |
Words |
Filter the current interactive search to tokens |
C-s M-c |
Comments |
Filter the current interactive search to comments |
C-s M-s |
Strings |
Filter the current interactive search to strings |
Scheme
| Command |
Keybinding |
Description |
| harmonia-scheme-mode |
|
Switches to harmonia-scheme-mode in the current buffer |
Cool
| Command |
Keybinding |
Description |
| harmonia-cool-mode |
|
Switches to harmonia-cool-mode in the current buffer |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode I-Search
| Command |
Filters To |
Description |
C-s M-t |
Class names |
Filter the current interactive search to class names |
C-s M-m |
Method names |
Filter the current interactive search to method names |
C-s M-v |
Variable names |
Filter the current interactive search to variable names |
C-s M-i |
Identifiers |
Filter the current interactive search to identifiers |
C-s M-w |
Words |
Filter the current interactive search to tokens |
C-s M-c |
Comments |
Filter the current interactive search to comments |
C-s M-s |
Strings |
Filter the current interactive search to strings |
Harmonia Settings
Harmonia-Mode uses the standard XEmacs "Customize" interface for user-level configuration. To get started, select either "Customize Harmonia-language" or "Customize Harmonia" from the Harmonia-Mode menu:
For example, selecting "Customize Harmonia" will bring you to a screen like this:
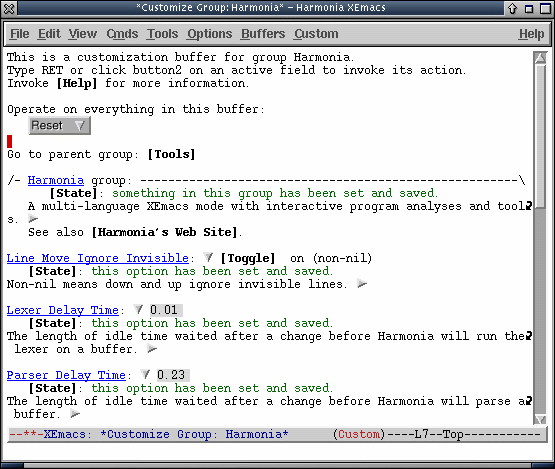
The XEmacs customization system is not described in detail here. To learn more about how to use it, see the XEmacs User's Manual.
Customization Groups
Harmonia-Mode's settings are divided into the following groups:
| Group Name |
Description |
| harmonia |
General options |
| harmonia-faces |
Fonts, sizes, colors, etc. used in Harmonia-Mode |
| harmonia-java-mode-faces |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Java mode (Only appears after a Java file has been loaded) |
| harmonia-titanium-mode-faces |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Titanium mode (Only appears after a Titanium file has been loaded) |
| harmonia-c-mode-faces |
A collection of faces for Harmonia C mode (Only appears after a C file has been loaded) |
| harmonia-cool-mode-faces |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Cool mode (Only appears after a Cool file has been loaded) |
| harmonia-scheme-mode-faces |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Scheme mode (Only appears after a Scheme file has been loaded) |
| harmonia-languages |
Contains links to the groups for each language. |
| harmonia-java |
Options specific to the Java language |
| harmonia-titanium |
Options specific to the Titanium language |
| harmonia-c |
Options specific to the C language |
| harmonia-cool |
Options specific to the Cool language |
| harmonia-scheme |
Options specific to the Scheme language |
The rest of this section describes each group's settings.
Group: Harmonia
The Harmonia group contains general options, as well as hyperlinks to the other, more specific, customization groups.
| Option |
Default |
Summary |
| Lexer Delay Time |
0.001 |
The length of idle time that Harmonia-Mode waits before running the Lexer after a text edit |
| Parser Delay Time |
0.5 |
The length of idle time that Harmonia-Mode waits between running the Lexer and the Parser |
| Sematics Delay Time |
0.4 |
The length of idle time that Harmonia-Mode waits between running the Parser and Semantics |
| Line Move Ignore Invisible |
Off |
(XEmacs Option) Non-nil means down and up arrow ignore invisible lines |
| Clean Up On Exit |
On |
Whether or not to erase all formatting when switching out of harmonia-mode to a different major mode |
| Auto-Recenter Buffer During Structural Movement |
Off |
Whether or not the screen should be forced to recenter after structural movement commands |
| Persistent I-Search Structural Filters |
Off |
Whether or not structural filters should be reset between I-search sessions |
| Margin Width |
1 |
The width of the left margin (for error-triangles) in Harmonia-Mode buffers. |
| Warning Messages Enabled |
On |
Display warnings about source code detected by semantic analysis |
Group: Harmonia Faces
A collection of faces used to highlight various sections of `harmonia-mode' buffers. Many of these are prefixed with `font-lock', for consistent access in the "edit faces" screen.
| Option |
Summary |
| Harmonia Nav Structure Face |
Harmonia-Mode face used to highlight the currently navigated structure. |
| Harmonia Error Face |
Harmonia-Mode face used to highlight errors. |
| Harmonia Error Icon Face |
Harmonia-Mode face used to color the triangle in the margin that indicates program errors. |
| Harmonia Warning Face |
Harmonia-Mode face used to highlight warnings. |
| Harmonia Warning Icon Face |
Harmonia-Mode face used to color the exclamation point in the margin that indicates program warnings. |
| Harmonia Preprocessor Face |
Harmonia-Mode face used to highlight preprocessed includes in the buffer (only for C mode). |
| Harmonia Java Mode Faces (Sub-Group) |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Java mode |
| Harmonia Titanium Mode Faces (Sub-Group) |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Titanium mode |
| Harmonia C Mode Faces (Sub-Group) |
A collection of faces for Harmonia C mode |
| Harmonia Cool Mode Faces (Sub-Group) |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Cool mode |
| Harmonia Scheme Mode Faces (Sub-Group) |
A collection of faces for Harmonia Scheme mode |
Group: Harmonia Java Faces
A collection of faces used to highlight various sections of `harmonia-java-mode' buffers. Many of these are prefixed with `font-lock', for consistent access in the "edit faces" screen.
| Option |
Summary |
| Harmonia Java Method Name Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for method names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-function-name-face |
| Harmonia Java Variable Name Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for variable names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-variable-name-face |
| Harmonia Java Type Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for type names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia Java Comment Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for comments.
Defaults to 'font-lock-comment-face |
| Harmonia Java String Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for strings.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
| Harmonia Java Special Literal Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for special literals (null, true, false).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Java Special Var Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for special variables (this, super).
Defaults to 'font-lock-reference-face |
| Harmonia Java Control Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for control constructs (for, while, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Java Declarator Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for declarators (class, interface, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Java Modifier Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for type modifiers (abstract, final, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia Java Pragma Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for compilation pragmas (import, package).
Defaults to 'font-lock-preprocessor-face |
| Harmonia Java Public Access Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for 'public' modifier.
Defaults to 'font-lock-reference-face |
| Harmonia Java Protected Access Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for 'protected' modifier.
Defaults to 'font-lock-preprocessor-face |
| Harmonia Java Private Access Face |
Harmonia-Java-Mode face for 'private' modifier.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
Group: Harmonia Titanium Faces
A collection of faces used to highlight various sections of `harmonia-titanium-mode' buffers. Many of these are prefixed with `font-lock', for consistent access in the "edit faces" screen.
| Option |
Summary |
| Harmonia Titanium Method Name Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for method names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-function-name-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Variable Name Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for variable names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-variable-name-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Type Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for type names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Comment Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for comments.
Defaults to 'font-lock-comment-face |
| Harmonia Titanium String Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for strings.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Special Literal Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for special literals (null, true, false).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Special Var Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for special variables (this, super).
Defaults to 'font-lock-reference-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Control Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for control constructs (for, while, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Declarator Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for declarators (class, interface, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Modifier Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for type modifiers (abstract, final, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Pragma Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for compilation pragmas (import, package).
Defaults to 'font-lock-preprocessor-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Public Access Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for 'public' modifier.
Defaults to 'font-lock-reference-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Protected Access Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for 'protected' modifier.
Defaults to 'font-lock-preprocessor-face |
| Harmonia Titanium Private Access Face |
Harmonia-Titanium-Mode face for 'private' modifier.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
Group: Harmonia C Faces
A collection of faces used to highlight various sections of `harmonia-c-mode' buffers. Many of these are prefixed with `font-lock', for consistent access in the "edit faces" screen.
| Option |
Summary |
| Harmonia C Function Name Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for function names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-function-name-face |
| Harmonia C Function Call Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for function calls.
Defaults to 'font-lock-variable-name-face |
| Harmonia C Variable Name Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for variable names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-variable-name-face |
| Harmonia C Type Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for type names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia C Comment Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for comments.
Defaults to 'font-lock-comment-face |
| Harmonia C String Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for strings.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
| Harmonia C Control Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for control constructs (for, while, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-name-face |
| Harmonia C Declarator Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for declarators (struct, enum, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-name-face |
| Harmonia C Modifier Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for type modifiers (register, static, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia C Preproc Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for preprocessor directives.
Defaults to 'font-lock-preprocessor-name-face |
Group: Harmonia Cool Faces
A collection of faces used to highlight various sections of `harmonia-cool-mode' buffers. Many of these are prefixed with `font-lock', for consistent access in the "edit faces" screen.
| Option |
Summary |
| Harmonia Cool Method Name Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for method names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-function-name-face |
| Harmonia Cool Variable Name Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for variable names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-variable-name-face |
| Harmonia Cool Type Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for type names.
Defaults to 'font-lock-type-face |
| Harmonia Cool Comment Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for comments.
Defaults to 'font-lock-comment-face |
| Harmonia Cool String Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for strings.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
| Harmonia Cool Special Literal Face |
Harmonia-C-Mode face for special literals (null, true, false).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Cool Control Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for control constructs (if, while, loop, etc.).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
| Harmonia Cool Declarator Face |
Harmonia-Cool-Mode face for declarators (class, inherits).
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-face |
Group: Harmonia Scheme Faces
A collection of faces used to highlight various sections of `harmonia-scheme-mode' buffers. Many of these are prefixed with `font-lock', for consistent access in the "edit faces" screen.
| Option |
Summary |
| Harmonia Scheme Function Def Name Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for function names in definitions.
Defaults to 'font-lock-function-name-face |
| Harmonia Scheme Variable Def Name Call Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for variable names in definitions.
Defaults to 'font-lock-variable-name-face |
| Harmonia Scheme Special Forms Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for special form keywords.
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-name-face |
| Harmonia Scheme Comment Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for comments.
Defaults to 'font-lock-comment-face |
| Harmonia Scheme String Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for characters and strings.
Defaults to 'font-lock-string-face |
| Harmonia Scheme Id Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for identifiers.
Defaults to 'font-lock-keyword-name-face |
| Harmonia Scheme Literal Face |
Harmonia-Scheme-Mode face for number and boolean literals.
Defaults to 'font-lock-reference-name-face |
Group: Harmonia Languages
All Harmonia languages
| Group |
Description |
| harmonia-cool |
Options specific to the Cool language |
| harmonia-java |
Options specific to the Java language |
| harmonia-titanium |
Options specific to the Titanium language |
| harmonia-c |
Options specific to the C language |
| harmonia-scheme |
Options specific to the Scheme language |
Group: Harmonia Cool Mode
Options for Harmonia Cool Mode
| Setting |
Description |
| Harmonia-Cool-Mode Enabled |
Automatically starts harmonia-cool-mode when opening a file with a matching filename. This adds the Cool language to `auto-mode-alist'. Note that this can usually be overridden with a "-*- mode: some mode -*-" line at the beginning of a file. |
| Harmonia-Cool-Mode File Extensions |
A list of Cool file extensions that trigger XEmacs to invoke Harmonia-Cool-Mode.
Defaults to *.cl |
| Harmonia-Cool-Mode Max File-Size |
If a Cool file is smaller than this limit (in bytes), Harmonia-Cool-Mode will automatically be invoked. If the file is bigger, Harmonia-Cool-Mode will not be started.
Defaults to 200,000 bytes. |
Group: Harmonia Java Mode
Options for Harmonia Java Mode
| Setting |
Description |
| Harmonia-Java-Mode Enabled |
Automatically starts harmonia-java-mode when opening a file with a matching filename. This adds the Java language to `auto-mode-alist'. Note that this can usually be overridden with a "-*- mode: some mode -*-" line at the beginning of a file. |
| Harmonia-Java-Mode File Extensions |
A list of java file extensions that trigger XEmacs to invoke Harmonia-Java-Mode.
Defaults to *.java |
| Harmonia-Java-Mode Max File-Size |
If a Java file is smaller than this limit (in bytes), Harmonia-Java-Mode will automatically be invoked. If the file is bigger, Harmonia-Java-Mode will not be started.
Defaults to 200,000 bytes. |
| JDK Path |
Path to the JDK source code.
Harmonia-Java's semantic analyses need the source code for a JDK to work properly. Install the source code for a JDK (any version) and set this to the path of the src/ directory in that installation. In a typical installation, you would unpack the src.jar file included with Sun's JDK and point JDK Path at that directory. |
| Project Path |
Path to current project's source code.
Harmonia-Java's semantic analyses need to know where project code is located. If your Java files import other Java files, add the paths to the imported file's directories here.
Defaults to the current directory '.' |
| Cache Directory |
Path to semantic cache directory.
Harmonia-mode for Java caches its semantic analysis results (name resolution and type checking) in your home directory, in a new subdirectory identified by this customization variable. This cache speeds analysis immensely, and only requires around 1-2 KB of data per analyzed Java class.
Defaults to ~/.harmonia_java_cache. |
| Read-Only Cache Directories |
Path to read-only semantic cache directories.
Harmonia-Java's semantic analyses can search for pre-cached data in additional directories before searching in the cache directory. |
| Project Files |
Files to always load.
In some cases, files are not always loaded when they are needed. This can occur when the filenames and the classes in them do not match up properly. These files will always be loaded for semantic analysis, but only upon creation of the symbol table. In particular, changing this variable will not load files until you restart XEmacs. These files are not cached. (This variable is temporary, and will be removed in a future release.) |
| Always Run Semantics |
Force semantics to continue even if the JDK is not correct or present. If you do not have a JDK source distribution installed, or your JDK distribution is broken in some way, but you still want semantics to run, set this to true. |
| Java Mode Faces |
A collection of face for Harmonia Java Mode |
Group: Harmonia Titanium Mode
Options for Harmonia Titanium Mode
| Setting |
Description |
| Harmonia-Titanium-Mode Enabled |
Automatically starts harmonia-titanium-mode when opening a file with a matching filename. This adds the Titanium language to `auto-mode-alist'. Note that this can usually be overridden with a "-*- mode: some mode
-*-" line at the beginning of a file. |
| Harmonia-Titanium-Mode File Extensions |
A list of java file extensions that trigger XEmacs to invoke Harmonia-Titanium-Mode.
Defaults to *.ti |
| Harmonia-Titanium-Mode Max File-Size |
If a Titanium file is smaller than this limit (in bytes), Harmonia-Titanium-Mode will automatically be invoked. If the file is bigger, Harmonia-Titanium-Mode will not be started.
Defaults to 200,000 bytes. |
| TDK Path |
Path to the TDK source code.
Harmonia-Titanium's semantic analyses need the source code for a TDK to work properly. Install the source code for a TDK (any version) and set this to the path of the src/ directory in that installation. In a typical installation, you copy the tlib directory from the Titanium compiler distribution and point JDK Path at that directory. The default Harmonia installation provides this for you.
Defaults to the default install location for the TDK |
| Project Path |
Path to current project's source code.
Harmonia-Titanium's semantic analyses need to know where project code is located. If your Titanium files import other Titanium or Java files, add the paths to the imported file's directories here.
Defaults to the current directory '.' |
| Cache Directory |
Path to semantic cache directory.
Harmonia-mode for Titanium caches its semantic analysis results (name resolution and type checking) in your home directory, in a new subdirectory identified by this customization variable. This cache speeds analysis immensely, and only requires around 1-2 KB of data per analyzed Titanium class.
Defaults to ~/.harmonia_titanium_cache. |
| Read-Only Cache Directories |
Path to read-only semantic cache directories.
Harmonia-Titanium's semantic analyses can search for pre-cached data in additional directories before searching in the cache directory. |
| Project Files |
Files to always load.
In some cases, files are not always loaded when they are needed. This can occur when the filenames and the classes in them do not match up properly. These files will always be loaded for semantic analysis, but only upon creation of the symbol table. In particular, changing this variable will not load files until you restart XEmacs. These files are not cached. (This variable is temporary, and will be removed in a future release.) |
| Always Run Semantics |
Force semantics to continue even if the TDK is not correct or present. If you do not have a TDK source distribution installed, or your TDK distribution is broken in some way, but you still want semantics to run, set this to true. |
| Titanium Mode Faces |
A collection of face for Harmonia Titanium Mode |
Group: Harmonia C Mode
Options for Harmonia C Mode
| Setting |
Description |
| Harmonia-C-Mode Enabled |
Automatically starts harmonia-c-mode when opening a file with a matching filename. This adds the C language to `auto-mode-alist'. Note that this can usually be overridden with a "-*- mode: some mode
-*-" line at the beginning of a file. |
| Harmonia-C-Mode File Extensions |
A list of C file extensions that trigger XEmacs to invoke Harmonia-C-Mode.
Defaults to *.c and *.h |
| Harmonia-C-Mode Max File-Size |
If a C file is smaller than this limit (in bytes), Harmonia-C-Mode will automatically be invoked.
If the file is bigger, Harmonia-C-Mode will not be started.
Defaults to 200,000 bytes. |
| GCC CPP |
Pathname to the C preprocessor binary.
Defaults to /usr/bin/gcc. |
| GCC CPP Flags |
Options for the C preprocessor.
Defaults to -E -C -dD -dI
These flags are required to make the C preprocessor work with gcc - do not change them unless you are using a different compiler.
GCC version 3.0+ users can add -P to get rid of the #line directives. |
| GCC CPP Include Path |
Include path for the C preprocessor (e.g. -I/my/project/dir -I/her/project/dir) |
| Harmonia Preprocessor Shell |
Path to shell used by the Harmonia preprocessor facility (must include option to run shell with commands given on the the rest of the command line).
Defaults to /bin/bash -c |
| Harmonia Preprocessor Temporary Directory |
Path to temporary directory where the preprocessor can create, read, write and delete files.
Defaults to /tmp. |
Group: Harmonia Scheme Mode
Options for Harmonia Scheme Mode
| Setting |
Description |
| Harmonia-Scheme-Mode Enabled |
Automatically starts harmonia-scheme-mode when opening a file with a matching filename. This adds the Scheme language to `auto-mode-alist'. Note that this can usually be overridden with a "-*- mode: some mode
-*-" line at the beginning of a file. |
| Harmonia-Scheme-Mode File Extensions |
A list of Scheme file extensions that trigger XEmacs to invoke Harmonia-Scheme-Mode.
Defaults to *.scm |
| Harmonia-Scheme-Mode Max File-Size |
If a Scheme file is smaller than this limit (in bytes), Harmonia-Scheme-Mode will automatically be invoked.
If the file is bigger, Harmonia-Scheme-Mode will not be started.
Defaults to 200,000 bytes. |







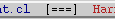
 .
.